Water Scarcity
California is a desert like climate.
Water levels are rising at a constant rate.
Global Warming could be a factor of this drought
.
Here's how you can make bold and italic text.
Here's how you can add an image:
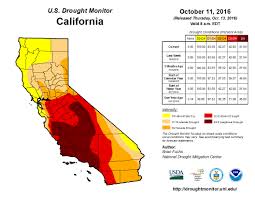
california drought
Here's how to make a list:
California drought
- California is a desert like climate.
Water levels are rising at a constant rate.
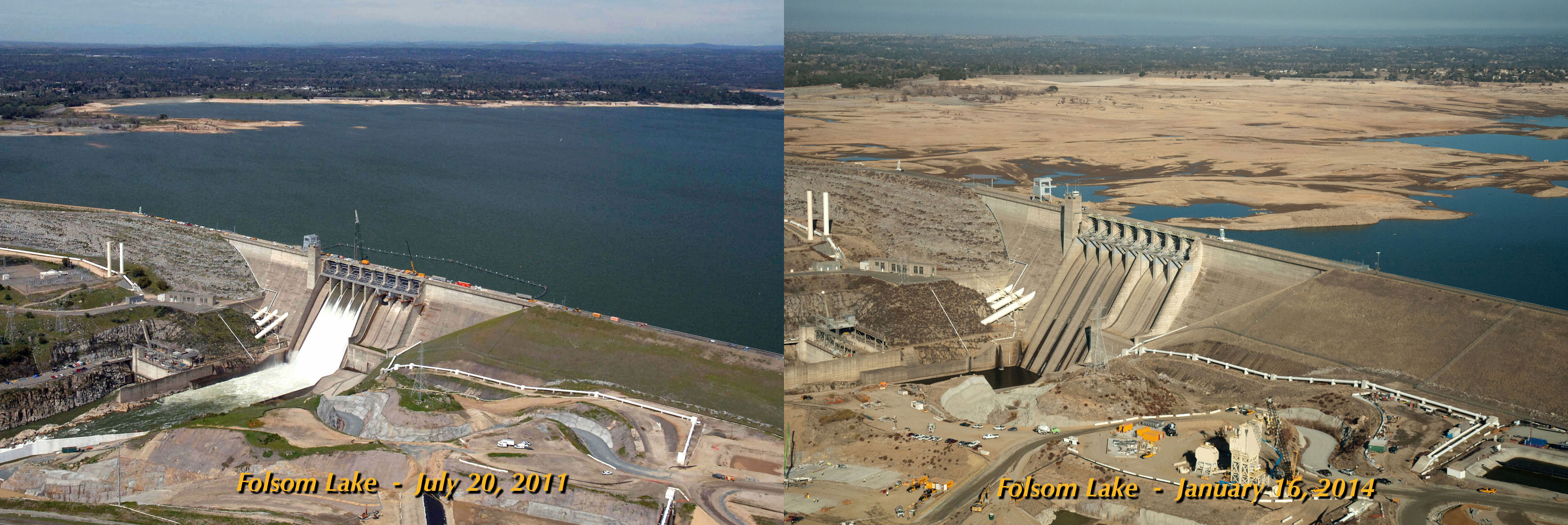
Global Warming could be a factor of this drought. A flood risk exists when Folsom Lake is above 60 percent. On March 7, 2016, Folsom Lake was at 68% capacity. The excess 8% of capacity is not allowed to be used 15 and had to be released to avoid potential property damage.
A spillway improvement is scheduled to be completed in 2017. This will allow short-term weather forecasts to be taken into consideration rather than using the crude 60% rule. This is possible because the river below the dam is wide enough to handle large releases on short notice.
The spillway improvement at Folsom lake is still under construction. Because the improvement is still under construction, 8000 acre-feet had to be released from Folsom Lake on March 7, 2016 to meet the US Army Corp of Engineers rule mandating a maximum 60 percent capacity during the winter.
On Tuesday, March 8, 2016, releases were scheduled to double from 8,000 CFS to 15,000 CFS. This resulted in 29,000 acre-feet in being released.
From March 7 to March 19, a cumulative 280,000 acre-feet of water was released into the Pacific Ocean via the Folsom Dam spillway.]
How we can solve this problem
- People are wasting water by sprinklers,long showers,water parks and old toilets.
Theyre necessary, but they’re ways we could stop wasting so much water by taking less time in the shower etc.
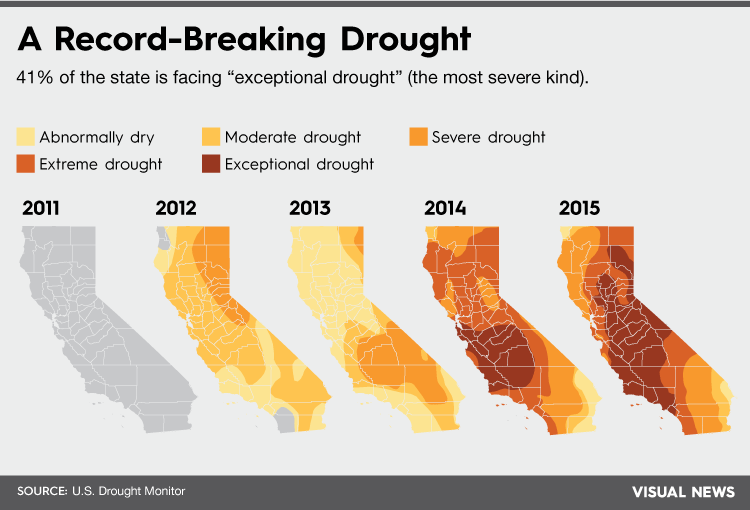
We could run out of water crops and water bills would be more expensive.The period between late 2011 and 2014 has been the driest in California history since record-keeping began.[42] In May 2015, one state resident poll conducted by Field Poll found that two out of three respondents agreed that it should be mandated for water agencies to reduce water consumption by 25%.
things we can do do help
- How can this problem be overcome?:By using less water everyday.
What are some of the best and worst case scenarios.2007–2009 saw three years of drought conditions, the 12th worst drought period in the state's history, and the first drought for which a statewide proclamation of emergency was issued. The drought of 2007–2009 also saw greatly reduced water diversions from the state water project. The summer of 2007 saw some of the worst wildfires in Southern California history.[41]
seasons
The 2015 prediction of an scientific method to bring rains to California is one contributor to ending the drought. In the spring of 2015, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration named the probability of the presence of El Niño conditions until the end of 2015 at 80%. Historically, sixteen winters between 1951 and 2015 have created El Niño. Six of those have had below-average rainfall, five had average rainfall, and five had above-average rainfall. However, as of May 2015, drought conditions have worsened and above average ocean temperatures have not created large storms.
The discharge and quality of water from California rivers and reservoirs have broad effects on factors such as water availability, and ecosystem system health. The discharge and quality also fluctuates on timescales ranging from minutes to centuries in complicated ways that seem random at first glance. By taking a large-scale view of these fluctuations and linking them to global scale climatic processes, researchers are beginning to see more structure and predictability than has been previously recognized. For example, the Nation's water resources are tied together on regional scales by their shared responses to temperature and precipitation variations. Understanding these links provides a better scientific basis for predicting and planning for droughts, floods, and water supplies, months to years in advance.
The California Water Science Center has installed webcams at several real-time streamgaging sites across the state. Webcams are another resource used to provide real-time surface-water information to scientists, emergency managers, and the general public.


Drought Impacts
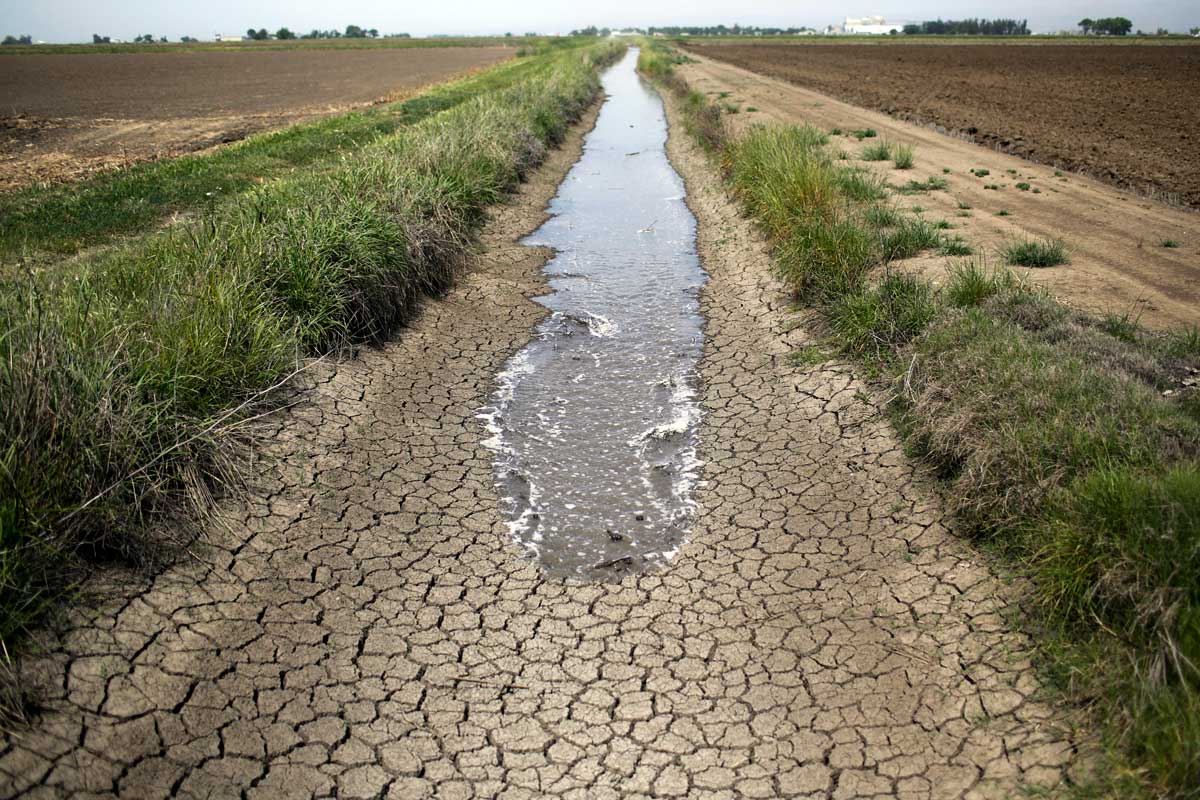
During times of drought, vegetation is visibly dry, stream and river flows decline, water levels in lakes and reservoirs fall, and the depth to water in wells increases. As drought persists, longer-term impacts can emerge, such as land subsidence, seawater intrusion, and damage to ecosystems. Unlike the immediate impacts of drought, however, long-term impacts can be harder to see, but more costly to manage in the future.During drought, declines in surface water flows can be detrimental to water supplies for agriculture and cities, hydropower production, navigation, recreation, and habitat for aquatic and riparian species. Several California Water Science Center streamgages have recently recorded streamflows that are below all-time record lows for specific days of the year. Annual runoff, which is calculated from this streamflow data, supplies many of our needs for water, Recent runoff estimates for California show measurements on par with 1930's and late 1970's droughts.
Unlike the effects of a drought on streamflows, groundwater levels in wells may not reflect a shortage of rainfall for a year or more after a drought begins. Despite reduced availability, reliance upon groundwater often increases during drought throughincreased groundwater pumping to meet water demands. If water is pumped at a faster rate than an aquifer is recharged by precipitation or other sources, water levels can drop, resulting in decreased water availability and deterioration of groundwater quality.
Ultimately, the surface water and groundwater form one interconnected hydrologic system. Nearly all surface water features - streams, lakes, reservoirs, wetlands, and estuaries - interact with groundwater. In addition to being a major source of water to lakes and wetlands, groundwater plays a crucial role in sustaining streamflow between precipitation events - especially during protracted dry periods. Although the contribution of groundwater to total streamflow varies widely among streams, hydrologists estimate the average contribution is somewhere between 40 and 50 percent.
To learn more HTML/CSS, check out these Impacted!







